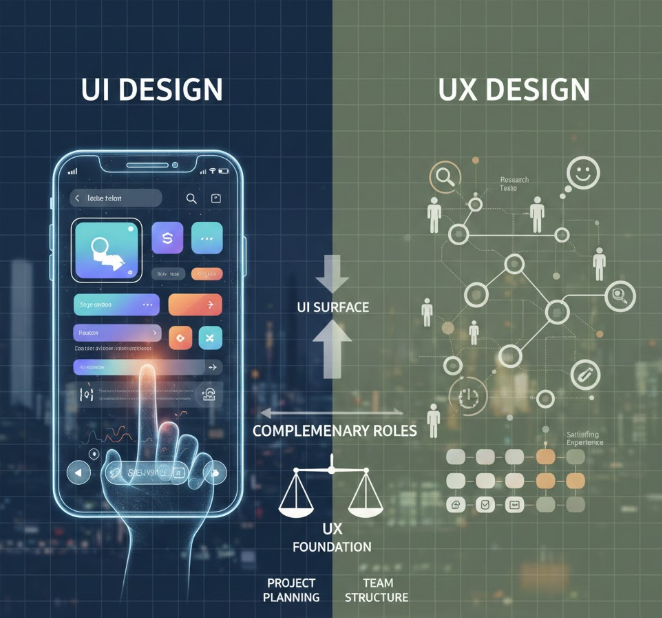
People often confuse UI vs. UX design because both shape digital experiences. However, they serve different purposes. UI handles the visual elements and interactive components. UX covers the entire user journey and satisfaction.
The distinction matters for business results. Companies that master both see higher conversions and better customer retention. Poor execution of either can cost thousands in lost revenue.
In the next section, we’ll break down the differences in detail and show why each truly matters for your business. You’ll get a clear, step-by-step understanding of UI vs UX.
What UI Design Means
UI design focuses on the visual interface users interact with on screens. It covers every element that users see and touch. Buttons, colors, typography, icons, and layouts all fall under UI design.
The goal is to create interfaces that look professional and feel intuitive. Core elements of user interface design:
- Visual hierarchy that guides user attention
- Color schemes that reflect brand identity
- Typography that enhances readability
- Interactive buttons and form fields
- Consistent spacing and alignment
- Icons and graphics that communicate clearly
UI designers make digital products visually appealing. They select colors that match brand guidelines. They choose fonts that users can read easily. They design buttons that users want to click.
The user interface acts as the bridge between people and technology. A well-designed UI makes complex actions feel simple. Users should complete tasks without confusion or frustration.
Consider an e-commerce checkout page. The UI designer decides where the payment button appears. They choose its color, size, and text. They arrange form fields in logical order. They add visual feedback when users complete steps.
Impact on business performance:
Research shows that 94% of first impressions relate to design. Users form opinions in just 50 milliseconds. A poorly designed interface drives visitors away before they explore your product.
The visual design creates trust. Clean interfaces signal professionalism and reliability. Cluttered screens suggest disorganization and poor quality. Users make these judgments instantly.
UI design affects conversion rates directly. Clear call-to-action buttons increase clicks. Readable text reduces bounce rates. Consistent design elements build brand recognition.
Companies with strong UI see measurable results. Studies indicate that good UI can boost conversion rates by 200%. The visual appeal keeps users engaged and encourages action.
UI Design Process Steps
Professional UI designers follow structured methods. They start with wireframes that map basic layouts. They create mockups that show visual details. They build prototypes for testing interactions.
Each iteration refines the interface. Designers test color combinations for accessibility. They adjust spacing to improve readability. They modify elements based on user feedback.
Common UI Components
Modern interfaces share standard elements. Navigation menus help users move between pages. Search bars let users find specific content. Progress indicators show task completion. Modal windows display important information.
These components follow established patterns. Users expect certain elements in specific locations. The logo typically appears in the top left corner. Navigation sits at the top or side. This consistency reduces cognitive load.
What UX Design Means
UX design encompasses the complete user experience with a product or service.
User experience design goes deeper than visual appeal. It examines how users feel throughout their entire journey.
From first contact to final interaction, UX covers every touchpoint. Key aspects of user experience design:
- User research and behavior analysis
- Information architecture and content structure
- User flow and task completion paths
- Wireframe and prototype development
- Usability testing with real users
- Continuous improvement based on data
UX designers act as user advocates. They identify pain points that frustrate customers. They find opportunities to improve efficiency. They ensure products solve real problems.
The work starts before any visual design begins. UX designers conduct research to understand target audiences. They interview users about needs and preferences. They analyze competitor products. They map user journeys.
Consider a banking app. UX designers study how customers manage money. They identify common tasks like checking balances and transferring funds. They map the steps users take to complete these actions.
Research-driven approach:
UX design relies on data, not assumptions. Designers create user personas based on actual customer profiles. These personas represent different user types with specific goals and challenges.
They develop user stories that describe desired outcomes. A story might state: “As a busy professional, I want to transfer money quickly so I can focus on my work.”
Designers test prototypes with real users. They observe where people get confused. They measure how long tasks take. They gather feedback about satisfaction levels.
UX Design Process Stages
The UX design process follows clear phases. Research comes first to understand user needs. Designers then define problems worth solving. They ideate multiple solutions. They prototype and test repeatedly.
Each stage builds on the previous one. Early research informs design decisions. Testing reveals what works and what fails. Iteration leads to better solutions.
Information architecture organizes content logically. UX designers decide which features users need most. They create navigation systems that make sense. They reduce steps required to complete actions.
Measuring UX Success
Good UX produces measurable outcomes. User satisfaction scores increase. Task completion rates improve. Support tickets decrease. Return visitor numbers grow.
These metrics prove design effectiveness. They justify investment in UX improvements. They guide future design decisions.
UI vs UX: Key Differences Explained
UI versus UX design serves distinct but complementary roles. The differences matter for project planning and team structure. Understanding each discipline helps businesses allocate resources effectively.
| Aspect | UI Design | UX Design |
| Focus | Visual interface elements | Overall user experience |
| Scope | What users see and touch | Complete user journey |
| Goal | Attractive, functional interfaces | Efficient, satisfying experiences |
| Process | Visual design and prototyping | Research, testing, iteration |
| Output | Style guides, mockups, components | Wireframes, prototypes, user flows |
| Skills | Visual design, typography, color theory | Research, analysis, problem-solving |
UI creates the surface layer. It handles aesthetics and interactivity. Every button, image, and animation falls under UI. The discipline requires strong visual design skills.
UX builds the foundation. It solves user problems through research and testing. UX designers map entire experiences. They need analytical and empathetic abilities.
Analogy for clarity:
Think of a restaurant. UX design represents the complete dining experience. This includes reservation ease, wait times, menu clarity, service quality, and payment process. UI design covers the menu layout, plate presentation, and table settings.
Both elements must excel for success. Beautiful plating means nothing if the food tastes bad. Delicious food suffers from poor presentation. The combination creates memorable experiences.
Skill Set Comparison
UI designers need visual expertise. They master design tools like Figma and Adobe XD. They understand color psychology and visual hierarchy. They stay current with design trends.
UX designers need research skills. They conduct user interviews and analyze data. They also create information architectures, facilitate usability tests, and think systematically about user needs.
Career Path Differences
The roles require different training. UI designers often come from graphic design backgrounds. UX designers may have psychology or human-computer interaction degrees.
Both paths offer strong career prospects. The global UX market is projected to reach $32.95 billion by 2030. UI design market growth shows 15% annual increases.
How UI and UX Work Together
UI and UX design create better products through collaboration. Neither discipline succeeds in isolation. UI without UX produces pretty but frustrating interfaces. UX without UI delivers functional but unappealing products.
The relationship flows naturally. UX research identifies user needs, and these findings inform UI decisions. Visual design then brings UX concepts to life.
Collaboration process
UX designers start by mapping user journeys. They identify key tasks users need to complete. Then they create wireframes showing basic layouts and functionality.
UI designers take these wireframes forward. They add visual polish and brand personality. They design specific components and create interactive prototypes.
The teams work in constant feedback loops. UX insights guide UI choices. UI limitations inform UX solutions. Testing reveals when adjustments are needed.
Consider a mobile app redesign. UX designers research why users abandon shopping carts. For instance, they discover that checkout takes too many steps. They propose a streamlined three-step process.
UI designers visualize this new flow. They design clear progress indicators, create intuitive form fields, and add reassuring security badges. This combination reduces cart abandonment.
Real-World Examples
Successful products demonstrate this synergy. Spotify combines excellent UX with beautiful UI. The app understands music listener behavior. The interface makes playlist creation effortless and enjoyable.
Airbnb excels at both disciplines. UX research revealed booking anxiety. UI designers created trust through detailed photos and clear descriptions. The result transformed vacation rentals.
Amazon’s checkout process shows UX efficiency. The one-click purchase option removes friction. The UI design makes the button prominent and accessible. Sales increased significantly.
Integration Best Practices
Smart teams structure collaboration carefully. UX and UI designers attend the same meetings. They share research findings. They review each other’s work regularly.
Design systems unite both disciplines. These systems include UI components and UX patterns. Teams maintain consistency while allowing flexibility.
Regular user testing validates both aspects. Teams observe how users interact with visual elements. They measure whether the overall experience meets goals.
Why UI UX Matters for Business Results
UI UX design matters for business results because it increases conversions, reduces customer drop off, and improves long-term retention. A smooth user flow helps people finish actions faster, which raises sales and lowers support costs.
Clear layouts and simple interactions also build trust, which leads to repeat purchases and stronger brand recall. Here are the key benefits that explain why UI UX design will shape stronger business results in 2026.
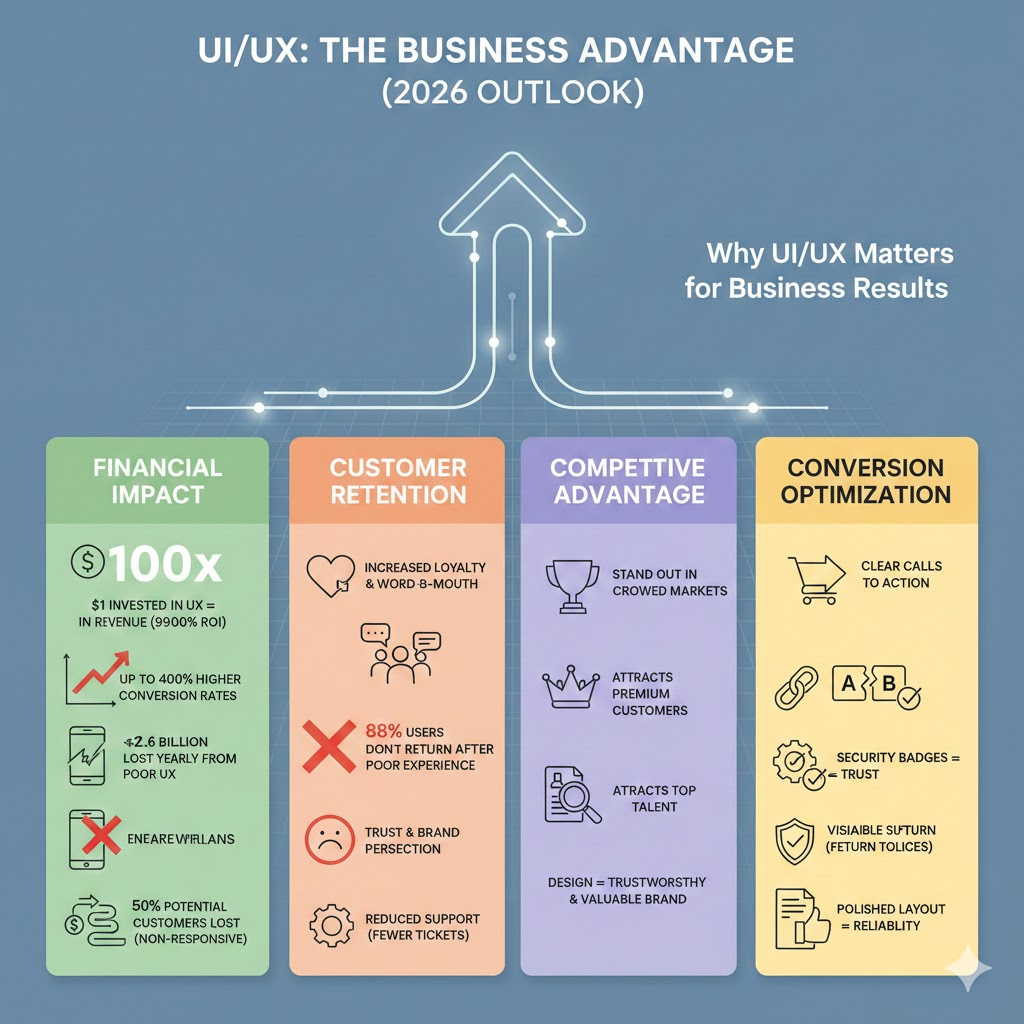
Financial impact statistics
Every dollar invested in UX returns $100 in revenue. This 9,900% ROI makes design one of the highest-performing business investments.
When the layout makes sense and actions feel simple, conversion rates can jump by up to 400% and customer acquisition costs drop without extra ad spend.
Now flip the story. Slow pages and awkward flows quietly drain revenue. Businesses lose $2.6 billion every year because users walk away from slow or frustrating sites, and a 1-second delay alone can cut conversions by 7%.
With more than 60% of web traffic coming from mobile devices, a non-responsive layout can erase nearly 50% of potential customers before they even meet your brand.
Customer Retention Impact
Good design builds loyalty because people return to products that feel easy and familiar. When users enjoy their experience, they also talk about it, and that naturally turns into word-of-mouth growth.
At the same time, research shows that 88% of users will not return after a poor experience, which means first impressions often decide long-term relationships. The quality of the interface also sends a quiet signal about the quality of the business itself.
On the support side, better design reduces confusion before problems even start. Clear layouts and simple navigation prevent mistakes, which means fewer tickets, faster resolutions, and lower support costs overall.
Competitive Advantage
In crowded markets, design becomes the quiet deal breaker. UI UX best practices help brands stand out because users can feel the difference between something that just exists and something that works well.
Companies known for strong design attract premium customers who are willing to pay more for better experiences. Over time, interface quality shapes brand perception and builds a reputation that feels more trustworthy and more valuable.
The impact reaches inside the company, too. Design-forward teams attract stronger talent because top professionals want to work where quality, clarity, and craft are taken seriously.
Conversion Optimization
When it comes to conversions, design shapes user behavior in subtle ways. Clear calls to action guide people toward the next step, while reduced friction removes the small frustrations that stop purchases.
A/B testing then turns design into a measurable growth tool by showing which choices actually increase conversion rates.
Trust also lives inside the interface. Security badges reduce purchase anxiety, visible return policies make first-time buyers feel safer, and a polished layout quietly communicates reliability before a single word is read.
Common UI UX Mistakes Businesses Make
Common UI UX mistakes that businesses often make are skipping user research, ignoring mobile users, inconsistent design, weak visual hierarchy, poor accessibility, and lack of testing. These errors frustrate users, reduce conversions, and harm brand perception.
Mistake 1: No User Research
Many companies assume they know what users want. They build products based on internal opinions, not actual user behavior. This often leads to features that don’t solve real problems. Users feel frustrated, confused, or ignored, which hurts engagement and loyalty.
Solution approach:
Interview real users, run surveys, and analyze competitor products. Build personas based on data, not assumptions. Test ideas early to prevent costly redesigns later.
Mistake 2: Poor Mobile Experience
Designing for desktop first ignores that most users are on mobile. Non-responsive or clunky mobile interfaces frustrate users. They leave quickly, which reduces conversions and damages brand reputation.
Solution approach:
Use mobile-first design. Test on actual devices and different screen sizes. Prioritize touch interactions and core functionality for a seamless experience.
Mistake 3: Inconsistent Design Elements
Random colors, buttons, and spacing confuse users. Inconsistent visuals make sites look unprofessional. Users struggle to predict actions, which reduces trust and engagement.
Solution approach:
Create a design system and style guide. Standardize components and usage rules. Consistency makes the interface predictable and comfortable.
Mistake 4: Slow Load Times
Heavy images, unoptimized code, and large scripts slow pages down. Users leave before engaging. This not only reduces conversions but also hurts SEO performance.
Solution approach:
Compress images and files. Use lazy loading for content below the fold. Monitor page speed and aim for under 2 seconds.
Mistake 5: Weak Visual Hierarchy
When everything looks equally important, users can’t focus. Important actions get lost, causing confusion and missed opportunities. Poor hierarchy makes scanning pages difficult.
Solution approach:
Use size, color, and placement to guide attention. Apply white space to separate sections. Design should follow natural eye movement.
Mistake 6: Ignoring Accessibility
Excluding users with disabilities limits your audience. Poor accessibility frustrates all users. It also reduces market reach and can harm SEO.
Solution approach:
Follow WCAG guidelines. Test with screen readers and keyboard navigation. Ensure proper color contrast and add alt text for images.
Mistake 7: No Testing Before Launch
Skipping testing leaves flaws for users to find. Teams often miss obvious issues because they are too close to the project. Post-launch fixes are expensive and damage user trust.
Solution approach:
Test early with prototypes. Conduct usability studies with target users. Use analytics to monitor drop-offs and iterate based on real behavior.
When to Hire a UI UX Design Agency
A business should hire a UI UX design agency when its product struggles to connect with real users, the internal team can’t solve key design problems, or when it needs specialized expertise to improve conversions, performance, and long-term growth. Agencies bring deep research, trend-aware design skills, and tested processes that internal teams often lack.
1. Users Are Leaving Without Taking Action
When analytics show high bounce rates, abandoned carts, or low engagement, it’s a clear sign that the design isn’t helping users complete goals. Users may click away before exploring because buttons are unclear, flows are confusing, or mobile views feel clunky.
At this point, hiring a UI UX design agency can help you analyze real user behavior, identify design bottlenecks, and restructure journeys to guide users toward key actions like signing up or purchasing.
Expert agencies use tools and user feedback to reduce friction and design experiences that feel intuitive instead of frustrating.
2. Your Product Feels Outdated or Untrustworthy
Design trends and user expectations evolve quickly, and what worked a few years ago might now make your product look stale or unprofessional. A dated interface can make visitors question the credibility of your brand before they even read a word.
A UI UX design agency evaluates your current visuals and interaction patterns, refreshing layouts, typography, and flows to reflect modern standards without losing your brand identity.
This helps make your product feel relevant and trustworthy again, which improves user retention and perception.
3. You’re Struggling With User Retention
Getting traffic is one thing, but keeping users engaged and returning is another. If users drop off after onboarding or repeatedly fail to navigate important parts of your product, the design might be the core issue.
Expertise from an agency helps you rethink onboarding flows, reduce friction in key interactions, and build engagement loops that keep users coming back.
Agencies can enhance readability, streamline interactions, and introduce micro-interactions that make your product feel far more satisfying to use.
4. Your Internal Team Lacks UI UX Expertise
Developers, marketers, and product managers are skilled in many areas, but UX design requires specialized knowledge in human behavior, research methods, and usability.
When your internal team tries to handle design as a side task, opportunities to improve core experiences are often missed.
A design agency brings dedicated researchers and designers with deep experience who can focus on understanding users, testing ideas, and shaping solutions that internal teams might never uncover on their own.
5. You’re Launching a New Product or Major Redesign
Big product launches or redesigns involve complex user flows, competing priorities, and high expectations. Internal teams often lack the bandwidth to research, test, and iterate while also managing other responsibilities.
A professional agency ensures that you don’t rush through crucial stages like discovery, prototyping, and testing.
Their structured process helps you launch faster and with fewer errors, and reduces the risk of costly revisions after release.
6. You Need Rapid Growth in Conversions
If your business is investing in marketing and traffic is increasing, but conversions aren’t keeping pace, design might be the bottleneck. Agencies specialize in optimizing key conversion points by simplifying layouts, clarifying calls-to-action, and reducing obstacles to purchase or signup.
Their holistic approach ensures that design changes align with business goals and user behavior patterns, driving measurable improvements in conversion performance.
7. You Want Cross-Device Consistency
With users accessing products on phones, tablets, and desktops, inconsistent experiences across devices can frustrate users and reduce loyalty. Agencies build responsive layouts that adapt interfaces fluidly across screen sizes.
This saves time and ensures that a user’s experience feels smooth, whether they are on mobile or desktop, which boosts satisfaction and loyalty.
8. You Need Scalability and Flexibility
Projects often grow beyond initial expectations, and internal teams may lack the headcount to scale up swiftly. Agencies offer flexibility, bringing in additional designers, researchers, or strategists as needed without long-term hiring commitments.
This allows your project to grow with demand while keeping costs predictable and focused on results.
9. You Want Objective, Data-Driven Design Decisions
Internal teams can get too close to a product and miss obvious usability issues. A quality UI UX agency brings objective analysis backed by research, testing, and industry trends.
Their decisions are rooted in data and real user feedback, not assumptions, which leads to design solutions that work for people rather than what “feels right” internally.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s more important, UI or UX?
UX is generally more important because it focuses on solving real user problems and making the product easy, efficient, and satisfying to use across the entire journey. UI is part of UX and makes the experience visually engaging, but if the experience is confusing or frustrating, users will leave regardless of how it looks.
What are the 7 principles of UI design?
The seven key UI design principles include visual hierarchy so users see the most important parts first, progressive disclosure that reveals info when needed, consistency in design and behavior, contrast between elements, proximity grouping related items, accessibility for diverse users, and alignment that organizes layout and navigation intuitively.
What is the first rule of UX?
The first rule of UX is to design around the user by understanding their goals, pain points, and context through research, so every design choice supports usability and helps users complete meaningful tasks without confusion or frustration. Prioritizing user needs ensures products feel natural, clear, and helpful.
What makes a good user interface?
A good user interface is intuitive so users understand it quickly, consistent so patterns are predictable, visible so users find what they need, and responsive so actions give clear feedback. It also supports accessibility, reduces cognitive effort, and guides users toward their goals with minimal friction.
Conclusion
UI vs UX design represents two essential but distinct disciplines. UI creates visual interfaces that users interact with directly. UX shapes the complete experience users have with products. Both matter tremendously for business success and customer satisfaction.
Companies that invest in both disciplines see remarkable returns. Higher conversion rates, increased revenue, and stronger brand loyalty all follow from excellent design. The statistics prove the business case convincingly.
The competitive advantage comes from getting both right. Users expect beautiful interfaces that work flawlessly. They abandon products that fail either test. Your design quality directly impacts your bottom line.
Ready to transform your digital presence with professional UI UX design? Contact six2eight today for a consultation. Our team delivers research-driven solutions that increase conversions and delight users.